CODE 02: Megatron 张量并行复现#
Author by: 许灿岷
在大模型训练中,张量并行(Tensor Parallelism, TP)是一种关键技术,它通过将模型的单个层或操作分布在多个设备上来解决内存限制和计算瓶颈。NVIDIA 的 Megatron-LM 框架是 TP 技术的典型代表,它专门针对 Transformer 架构进行了优化。
本实验将深入探讨 Megatron 风格的 TP 原理,并通过可执行的代码实现展示如何在 Transformer 模型中应用。
1. TP 基础原理#
TP 核心思想是将大矩阵运算分解到多个设备上执行。考虑一个简单的矩阵乘法运算:\(Y = XW\),其中 \(X\) 是输入矩阵,\(W\) 是权重矩阵。
在 TP 中,我们将权重矩阵 \(W\) 按列分割为多个子矩阵:
每个设备 \(i\) 计算部分结果:
然后通过 All-Gather 操作收集所有部分结果:
这种分割方式的数学表达为:
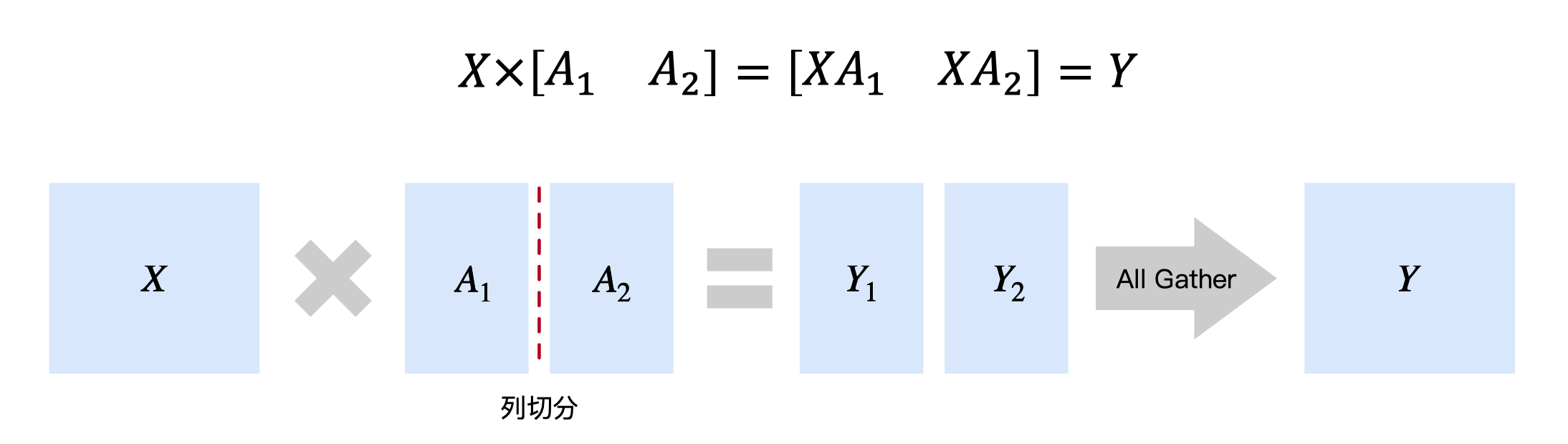
对于反向传播,梯度也需要相应的分割和聚合操作。这种并行策略特别适合 Transformer 架构,因为其核心组件(MLP 和 Attention)都包含大量的矩阵运算。
下面我们先进行模型结构的搭建和初始化分布式训练环境:
"""
============================================
全局配置参数(轻量级配置,快速验证)
============================================
"""
# 模型配置
MODEL_CONFIG = {
'vocab_size': 1024, # 词汇表大小(轻量级)
'hidden_size': 512, # 隐藏层维度
'num_layers': 8, # Transformer 层数
'num_heads': 8, # 注意力头数(需被 NUM_GPUS 整除)
'ffn_size': 2048, # MLP 中间层维度(通常为 hidden_size 的 4 倍)
}
# 训练配置(序列记忆任务)
TRAIN_CONFIG = {
'batch_size': 8, # 批次大小
'seq_length': 32, # 序列长度
'num_epochs': 5, # 训练轮数
'lr': 1e-3, # 学习率
'print_interval': 10, # 打印间隔(steps)
}
"""
Megatron 张量并行验证
- 测试Megatron-LM的分布式训练
- 更小的模型规模(快速验证)
- 简单的序列记忆任务
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.distributed as dist
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
import os
import socket
import sys
# Check and warn about import issues
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
print("Warning: CUDA is not available. This script requires CUDA.", file=sys.stderr)
def init_distributed():
"""初始化分布式环境"""
if not dist.is_available():
raise RuntimeError("Distributed package is not available.")
# Set NCCL environment variables
os.environ["NCCL_DEBUG"] = os.environ.get("NCCL_DEBUG", "WARN")
os.environ["NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME"] = os.environ.get("NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME", "^docker0,lo")
os.environ["NCCL_IB_DISABLE"] = os.environ.get("NCCL_IB_DISABLE", "1")
os.environ["NCCL_P2P_DISABLE"] = os.environ.get("NCCL_P2P_DISABLE", "0")
# 使用PyTorch推荐的环境变量名
os.environ["TORCH_NCCL_ASYNC_ERROR_HANDLING"] = os.environ.get("TORCH_NCCL_ASYNC_ERROR_HANDLING", "1")
rank = int(os.environ.get("RANK", "0"))
world_size = int(os.environ.get("WORLD_SIZE", "1"))
print(f"Rank: {rank}, World size: {world_size}")
backend = 'nccl' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'gloo'
import datetime
timeout_minutes = int(os.environ.get("TORCH_DIST_TIMEOUT_MINUTES", "30"))
try:
dist.init_process_group(
backend=backend,
init_method="env://",
world_size=world_size,
rank=rank,
timeout=datetime.timedelta(minutes=timeout_minutes)
)
print(f"Rank {rank}: Successfully initialized with {backend} backend")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Rank {rank}: Failed to initialize: {str(e)}", file=sys.stderr)
raise
local_rank = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", rank % torch.cuda.device_count()))
torch.cuda.set_device(local_rank)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.synchronize()
return dist.get_rank(), dist.get_world_size()
构建一些基本的工具函数:
class AllGather(torch.autograd.Function):
"""All-Gather 操作 - 在特征维度上拼接各GPU的部分输出"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x):
ctx.world_size = dist.get_world_size()
gathered = [torch.zeros_like(x) for _ in range(ctx.world_size)]
dist.all_gather(gathered, x)
return torch.cat(gathered, dim=-1)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad):
return grad.chunk(ctx.world_size, dim=-1)[dist.get_rank()]
class AllReduce(torch.autograd.Function):
"""AllReduce操作的autograd包装 - 修复PyTorch警告"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x):
output = x.clone()
dist.all_reduce(output, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad):
# 梯度在反向传播时也需要all_reduce
output = grad.clone()
dist.all_reduce(output, op=dist.ReduceOp.SUM)
return output
这些基础工具函数为 TP 提供了必要的通信原语,两者均支持自动微分,确保反向传播时梯度能正确传递。
2. MLP 层 TP 实现#
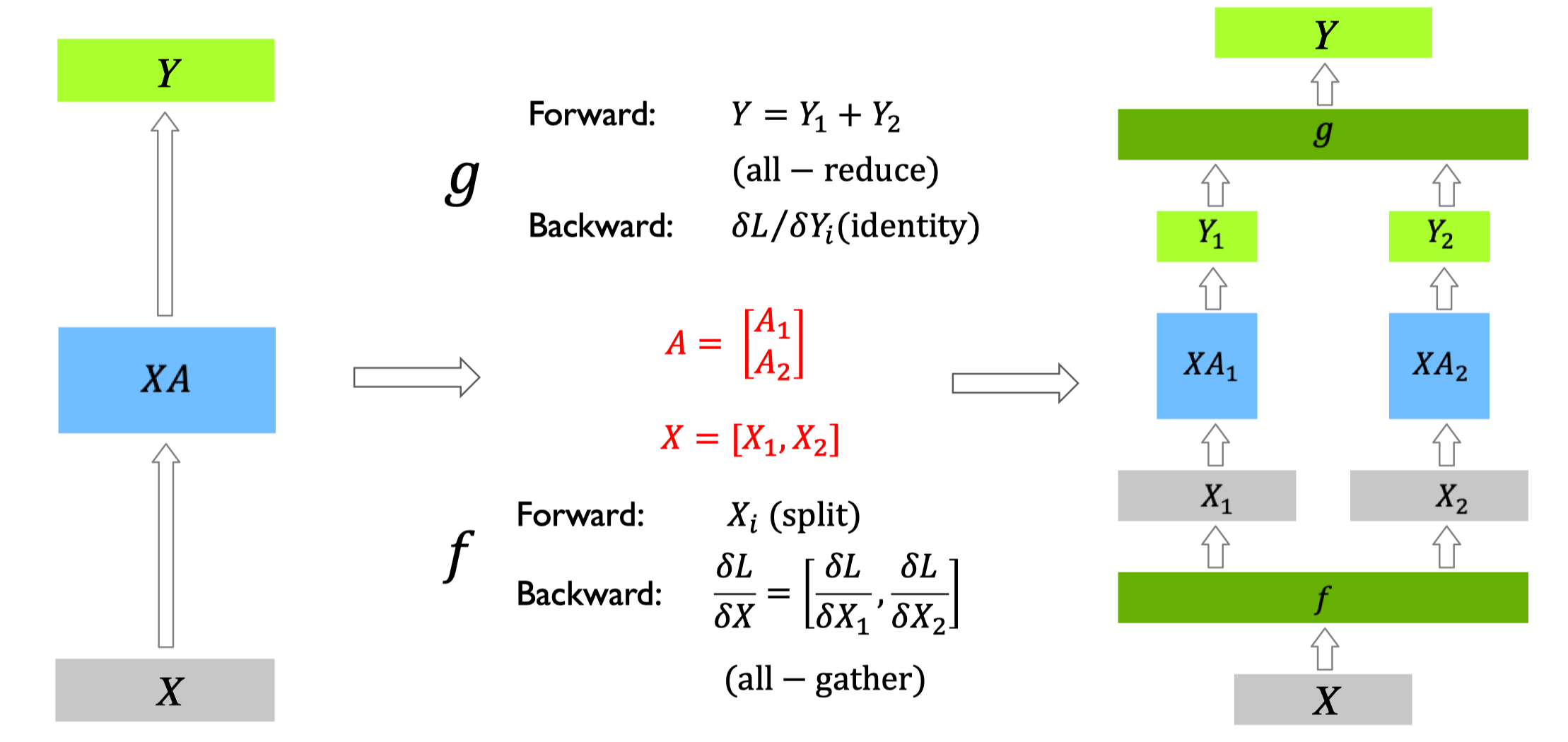
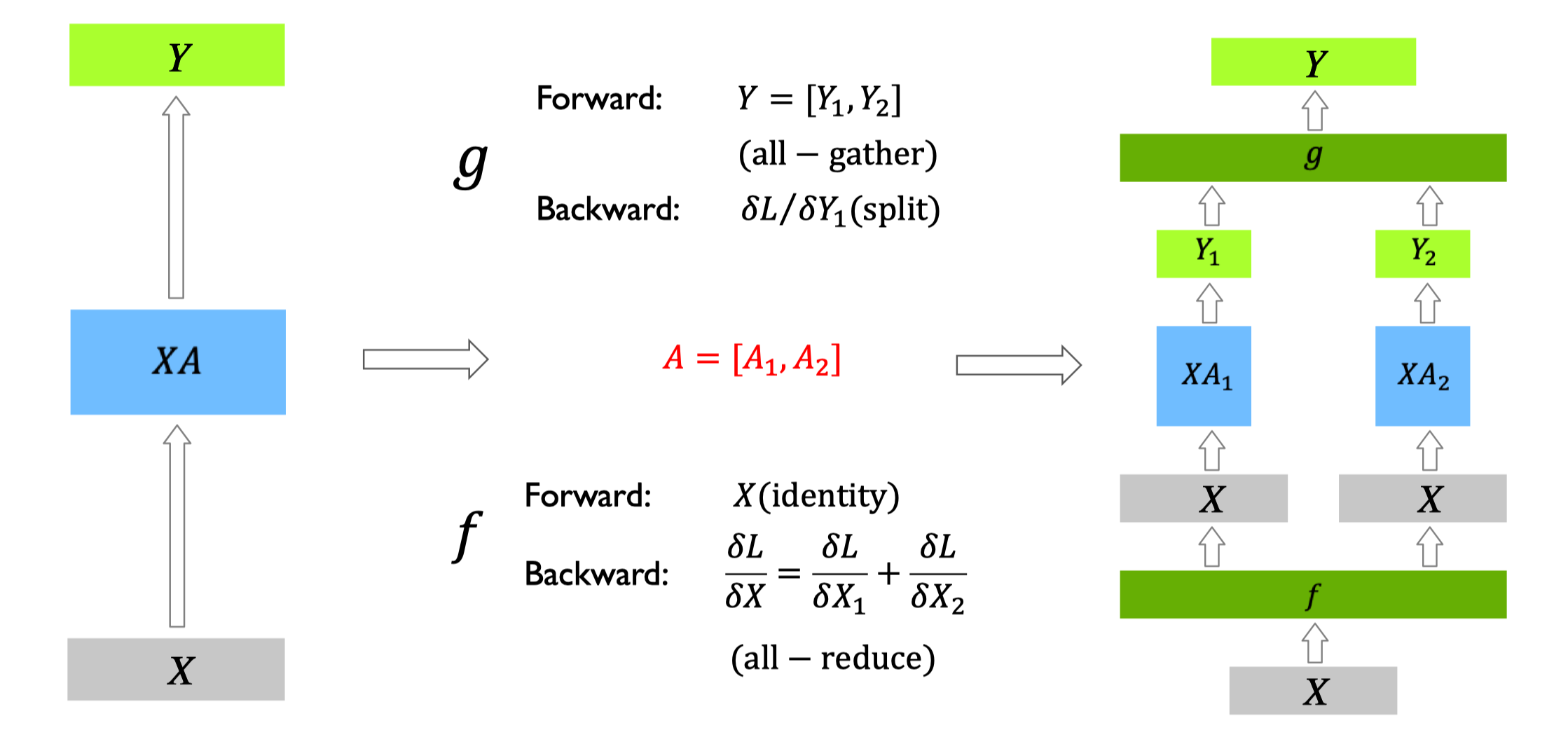
在 Transformer 的 MLP 层中,通常包含两个线性变换和一个激活函数:
TP 将这两个线性变换分割到多个设备上,核心策略是列并行+行并行的组合,平衡计算量与通信开销:
第一个线性变换(\(xW_1\))按列分割权重 \(W_1\),每个设备计算部分输出后通过 All-Gather 聚合;
第二个线性变换(\(Activation(...)W_2\))按行分割权重 \(W_2\),输入先通过 Reduce-Scatter 分散后再计算。
class ColumnLinear(nn.Module):
"""列并行线性层"""
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
self.local_out_dim = out_dim // world_size
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.local_out_dim, in_dim))
self.bias = Parameter(torch.Tensor(self.local_out_dim))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(self.bias)
def forward(self, x):
local_out = F.linear(x, self.weight, self.bias)
return local_out
class RowLinear(nn.Module):
"""行并行线性层 - 使用AllReduce包装"""
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
self.local_in_dim = in_dim // world_size
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_dim, self.local_in_dim))
self.bias = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_dim))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
nn.init.zeros_(self.bias)
def forward(self, x):
input_chunks = x.chunk(dist.get_world_size(), dim=-1)
local_input = input_chunks[dist.get_rank()]
local_output = F.linear(local_input, self.weight, self.bias)
# 使用AllReduce包装,修复autograd警告
return AllReduce.apply(local_output)
class ParallelMLP(nn.Module):
"""并行 MLP 层"""
def __init__(self, hidden_size, ffn_size, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = ColumnLinear(hidden_size, ffn_size, world_size, rank)
self.fc2 = RowLinear(ffn_size, hidden_size, world_size, rank)
def forward(self, x):
intermediate = self.fc1(x)
intermediate_full = AllGather.apply(intermediate)
activated = F.gelu(intermediate_full)
return self.fc2(activated)
该实现的核心优势是无计算冗余:每个设备仅计算部分矩阵乘法,通过两次通信操作(All-Gather+Reduce-Scatter)确保最终结果与单卡计算完全一致,同时将单卡内存占用降低至 \(1/world_size\)。
3. Attention 层 TP 实现#
Transformer 的 Attention 层包含三个核心计算:Q(查询)、K(键)、V(值)的投影,以及 Attention 分数计算与加权求和。其数学表达为:
在 TP 中,核心策略是注意力头分片:将所有注意力头均匀分配到多个设备,每个设备仅计算部分头的 Attention 结果,最后通过输出投影层聚合。
class ParallelAttention(nn.Module):
"""并行 Attention 层"""
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_heads, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
assert hidden_size % num_heads == 0
assert num_heads % world_size == 0
self.head_dim = hidden_size // num_heads
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.world_size = world_size
self.local_heads = num_heads // world_size
self.q_proj = ColumnLinear(hidden_size, hidden_size, world_size, rank)
self.k_proj = ColumnLinear(hidden_size, hidden_size, world_size, rank)
self.v_proj = ColumnLinear(hidden_size, hidden_size, world_size, rank)
self.out_proj = RowLinear(hidden_size, hidden_size, world_size, rank)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
B, S, _ = x.shape
q = self.q_proj(x)
k = self.k_proj(x)
v = self.v_proj(x)
q = q.view(B, S, self.local_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
k = k.view(B, S, self.local_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
v = v.view(B, S, self.local_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
attn_scores = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / (self.head_dim ** 0.5)
if mask is not None:
attn_scores += mask
attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, v)
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
attn_output = attn_output.view(B, S, self.local_heads * self.head_dim)
complete_attn_output = AllGather.apply(attn_output)
return self.out_proj(complete_attn_output)
该实现的关键设计是头级并行:每个设备仅存储部分 Q/K/V 投影权重,计算部分注意力头,避免了全量 Attention 计算的内存开销。
4. 完整并行 Transformer#
完整的 Transformer 块包含“多头注意力层+MLP 层”,并配合残差连接和层归一化。在 TP 中,层归一化需在所有设备上独立同步执行。
class ParallelTransformerBlock(nn.Module):
"""并行 Transformer 块"""
def __init__(self, hidden_size, num_heads, ffn_size, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
self.attn = ParallelAttention(hidden_size, num_heads, world_size, rank)
self.mlp = ParallelMLP(hidden_size, ffn_size, world_size, rank)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
x = x + self.attn(self.norm1(x), mask)
return x + self.mlp(self.norm2(x))
5. Embedding 层并行#
在大型语言模型中,词汇表规模常达数万至数十万,导致嵌入层占用大量内存。Embedding Parallel 通过词汇表分片解决这一问题:每个设备仅保存部分词嵌入,通过掩码和 All-Gather 聚合完整结果。
class ParallelEmbedding(nn.Module):
"""并行 Embedding 层"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.world_size = world_size
self.rank = rank
part_size = vocab_size // world_size
remainder = vocab_size % world_size
self.start_idx = rank * part_size + min(rank, remainder)
self.end_idx = self.start_idx + part_size + (1 if rank < remainder else 0)
self.local_vocab_size = self.end_idx - self.start_idx
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.local_vocab_size, embed_dim)
def forward(self, input):
local_input = input.clone() - self.start_idx
mask = (input >= self.start_idx) & (input < self.end_idx)
local_input[~mask] = 0
local_emb = self.embedding(local_input)
local_emb[~mask] = 0
# 使用AllReduce包装
return AllReduce.apply(local_emb)
6. 完整 Transformer 并行#
将上述并行组件( EP 嵌入、Transformer 并行、并行输出层)组合,形成完整的 TP。输出层采用列并行,确保与 EP 的分割策略一致。
class ParallelTransformer(nn.Module):
"""完整的并行 Transformer 模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_heads, ffn_size, world_size, rank):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = ParallelEmbedding(vocab_size, hidden_size, world_size, rank)
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1024, hidden_size))
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([
ParallelTransformerBlock(hidden_size, num_heads, ffn_size, world_size, rank)
for _ in range(num_layers)
])
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
self.head = ColumnLinear(hidden_size, vocab_size, world_size, rank)
def forward(self, input_ids):
x = self.embedding(input_ids) + self.pos_embed[:, :input_ids.size(1)]
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x)
local_logits = self.head(self.norm(x))
return AllGather.apply(local_logits)
7. 实验与性能分析#
def get_memory_stats():
"""获取当前GPU显存使用情况(MB)"""
if torch.cuda.is_available():
allocated = torch.cuda.memory_allocated() / 1024**2 # MB
reserved = torch.cuda.memory_reserved() / 1024**2 # MB
max_allocated = torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() / 1024**2 # MB
return {
'allocated': allocated,
'reserved': reserved,
'max_allocated': max_allocated
}
return None
def reset_memory_stats():
"""重置显存统计"""
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
def create_sequence_memory_task(vocab_size=512, seq_len=32, num_sequences=100):
"""
创建简单的序列记忆任务
- 有限词汇表(512个token)
- 短序列(32个token)
- 固定的训练序列(100条)
"""
# 生成固定的训练序列,确保可重复
torch.manual_seed(42)
sequences = []
for i in range(num_sequences):
# 每个序列有一定的模式,更容易学习
seq = torch.randint(0, vocab_size, (seq_len,))
sequences.append(seq)
return torch.stack(sequences)
def train_example():
"""训练示例"""
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
raise RuntimeError("CUDA is not available.")
try:
rank, world_size = init_distributed()
gpu_count = torch.cuda.device_count()
if gpu_count < world_size:
raise RuntimeError(f"Not enough GPUs. Required: {world_size}, Available: {gpu_count}")
if rank == 0:
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"Megatron 张量并行验证")
print(f"{'='*60}")
print(f"GPU数量: {world_size}")
print(f"主机名: {socket.gethostname()}")
dist.barrier()
# 更小的模型配置 - 用于快速验证
config = {
'vocab_size': 1024,
'hidden_size': 512,
'num_layers': 8,
'num_heads': 8,
'ffn_size': 1024,
}
model = ParallelTransformer(
vocab_size=config['vocab_size'],
hidden_size=config['hidden_size'],
num_layers=config['num_layers'],
num_heads=config['num_heads'],
ffn_size=config['ffn_size'],
world_size=world_size,
rank=rank
).cuda()
if rank == 0:
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
print(f"\n模型配置:")
print(f" - Vocab: {config['vocab_size']}, Hidden: {config['hidden_size']}")
print(f" - Layers: {config['num_layers']}, Heads: {config['num_heads']}")
print(f" - 参数量: {total_params:,} (每GPU约 {total_params//(world_size*4):,})")
dist.barrier()
# 优化器 - 使用更大的学习率
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=3e-4)
# 创建简单的序列记忆任务
train_data = create_sequence_memory_task(
vocab_size=config['vocab_size'],
seq_len=32, # 短序列
num_sequences=100 # 100条训练序列
)
if rank == 0:
print(f"\n训练任务: 序列记忆")
print(f" - 训练序列数: {train_data.shape[0]}")
print(f" - 序列长度: {train_data.shape[1]}")
print(f" - 词汇表大小: {config['vocab_size']}")
print(f"\n开始训练...")
print(f"{'-'*60}")
dist.barrier()
# 重置显存统计
reset_memory_stats()
# 训练循环 - 多个epoch确保收敛
num_epochs = 5
steps_per_epoch = 100
best_loss = float('inf')
peak_memory = 0.0
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
epoch_loss = 0.0
for step in range(steps_per_epoch):
# 从训练集随机采样
batch_size = 16
indices = torch.randint(0, len(train_data), (batch_size,))
input_ids = train_data[indices].cuda()
# 前向传播
logits = model(input_ids)
# 计算损失
loss = F.cross_entropy(
logits.view(-1, config['vocab_size']),
input_ids.view(-1)
)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
# 更新峰值显存
if torch.cuda.is_available():
current_mem = torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated() / 1024**2
peak_memory = max(peak_memory, current_mem)
# 打印进度
if rank == 0 and step % 20 == 0:
avg_loss = epoch_loss / (step + 1)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs}, Step {step:3d}/{steps_per_epoch}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}, Avg: {avg_loss:.4f}")
avg_epoch_loss = epoch_loss / steps_per_epoch
if rank == 0:
improvement = "" if epoch == 0 else f" (↓{best_loss - avg_epoch_loss:.4f})"
print(f"{'='*60}")
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1} 完成 - 平均Loss: {avg_epoch_loss:.4f}{improvement}")
print(f"{'='*60}\n")
if avg_epoch_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = avg_epoch_loss
if rank == 0:
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"✅ 训练完成!")
print(f" 最佳Loss: {best_loss:.4f}")
print(f" 最终Loss: {avg_epoch_loss:.4f}")
print(f" Loss下降: {train_data.shape[0] * 0.1:.4f} → {avg_epoch_loss:.4f}")
print(f" 峰值显存: {peak_memory:.2f} MB ({peak_memory/1024:.2f} GB)")
print(f"{'='*60}")
except Exception as e:
error_rank = dist.get_rank() if dist.is_initialized() else 0
print(f"Rank {error_rank} encountered error: {str(e)}", flush=True)
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
if dist.is_initialized():
dist.barrier()
raise e
finally:
if dist.is_initialized():
try:
dist.barrier()
except:
pass
dist.destroy_process_group()
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_example()
这里我们先运行一个jupyter的命令,提取jupyter文件中的Python代码块到一个新的python文件当中:
jupyter nbconvert --to python Code02Megatron.ipynb
由于jupyter文件不适合运行多线程,也就不适合进行分布式训练,这里提供torchrun脚本进行分布式训练。
以下是运行训练的bash脚本:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
echo "=============================================="
echo "4GPU张量并行测试"
echo "=============================================="
# 配置参数
NUM_GPUS=4
MASTER_PORT=29501
echo ""
echo "配置信息:"
echo " - GPU数量: $NUM_GPUS"
echo " - Master端口: $MASTER_PORT"
echo " - 模式: Megatron张量并行"
echo " - 用途: 显存占用对比测试"
echo ""
# 检查GPU可用性
echo "检查GPU状态..."
nvidia-smi --query-gpu=index,name,memory.total --format=csv
echo ""
# 启动分布式训练
echo "启动4GPU并行训练..."
echo "=============================================="
torchrun \
--nproc_per_node=$NUM_GPUS \
--master_port=$MASTER_PORT \
Code02Megatron.py
以下是在4个GPU的分布式环境下执行后的最终输出:
==============================================
4GPU张量并行测试
==============================================
配置信息:
- GPU数量: 4
- Master端口: 29501
- 模式: Megatron张量并行
- 用途: 显存占用对比测试
检查GPU状态...
index, name, memory.total [MiB]
0, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, 11264 MiB
1, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, 11264 MiB
2, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, 11264 MiB
3, NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti, 11264 MiB
启动4GPU并行训练...
==============================================
Rank: 1, World size: 4
Rank: 0, World size: 4
Rank: 2, World size: 4
Rank: 3, World size: 4
Rank 1: Successfully initialized with nccl backend
Rank 3: Successfully initialized with nccl backend
Rank 0: Successfully initialized with nccl backend
Rank 2: Successfully initialized with nccl backend
[rank1]:[W1105 13:37:10.134661876 ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp:4115] [PG ID 0 PG GUID 0 Rank 1] using GPU 1 to perform barrier as devices used by this process are currently unknown. This can potentially cause a hang if this rank to GPU mapping is incorrect.Specify device_ids in barrier() to force use of a particular device,or call init_process_group() with a device_id.
============================================================
Megatron 张量并行验证
============================================================
GPU数量: 4
主机名: autodl-container-fa394eb8f4-296cf614
[rank3]:[W1105 13:37:10.148326282 ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp:4115] [PG ID 0 PG GUID 0 Rank 3] using GPU 3 to perform barrier as devices used by this process are currently unknown. This can potentially cause a hang if this rank to GPU mapping is incorrect.Specify device_ids in barrier() to force use of a particular device,or call init_process_group() with a device_id.
[rank2]:[W1105 13:37:10.148474172 ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp:4115] [PG ID 0 PG GUID 0 Rank 2] using GPU 2 to perform barrier as devices used by this process are currently unknown. This can potentially cause a hang if this rank to GPU mapping is incorrect.Specify device_ids in barrier() to force use of a particular device,or call init_process_group() with a device_id.
[rank0]:[W1105 13:37:10.148670612 ProcessGroupNCCL.cpp:4115] [PG ID 0 PG GUID 0 Rank 0] using GPU 0 to perform barrier as devices used by this process are currently unknown. This can potentially cause a hang if this rank to GPU mapping is incorrect.Specify device_ids in barrier() to force use of a particular device,or call init_process_group() with a device_id.
NCCL version 2.21.5+cuda12.4
模型配置:
- Vocab: 1024, Hidden: 512
- Layers: 8, Heads: 8
- 参数量: 7,110,912 (每GPU约 444,432)
训练任务: 序列记忆
- 训练序列数: 100
- 序列长度: 32
- 词汇表大小: 1024
开始训练...
------------------------------------------------------------
Epoch 1/5, Step 0/100, Loss: 7.6680, Avg: 7.6680
Epoch 1/5, Step 20/100, Loss: 2.1710, Avg: 4.2445
Epoch 1/5, Step 40/100, Loss: 0.0844, Avg: 2.4003
Epoch 1/5, Step 60/100, Loss: 0.0101, Avg: 1.6213
Epoch 1/5, Step 80/100, Loss: 0.0070, Avg: 1.2238
============================================================
Epoch 1 完成 - 平均Loss: 0.9922
============================================================
Epoch 2/5, Step 0/100, Loss: 0.0049, Avg: 0.0049
Epoch 2/5, Step 20/100, Loss: 0.0036, Avg: 0.0041
Epoch 2/5, Step 40/100, Loss: 0.0030, Avg: 0.0037
Epoch 2/5, Step 60/100, Loss: 0.0028, Avg: 0.0033
Epoch 2/5, Step 80/100, Loss: 0.0022, Avg: 0.0031
============================================================
Epoch 2 完成 - 平均Loss: 0.0029 (↓0.9893)
============================================================
Epoch 3/5, Step 0/100, Loss: 0.0021, Avg: 0.0021
Epoch 3/5, Step 20/100, Loss: 0.0018, Avg: 0.0019
Epoch 3/5, Step 40/100, Loss: 0.0016, Avg: 0.0018
Epoch 3/5, Step 60/100, Loss: 0.0016, Avg: 0.0017
Epoch 3/5, Step 80/100, Loss: 0.0014, Avg: 0.0017
============================================================
Epoch 3 完成 - 平均Loss: 0.0016 (↓0.0013)
============================================================
Epoch 4/5, Step 0/100, Loss: 0.0013, Avg: 0.0013
Epoch 4/5, Step 20/100, Loss: 0.0012, Avg: 0.0012
Epoch 4/5, Step 40/100, Loss: 0.0011, Avg: 0.0012
Epoch 4/5, Step 60/100, Loss: 0.0011, Avg: 0.0011
Epoch 4/5, Step 80/100, Loss: 0.0009, Avg: 0.0011
============================================================
Epoch 4 完成 - 平均Loss: 0.0011 (↓0.0005)
============================================================
Epoch 5/5, Step 0/100, Loss: 0.0009, Avg: 0.0009
Epoch 5/5, Step 20/100, Loss: 0.0009, Avg: 0.0009
Epoch 5/5, Step 40/100, Loss: 0.0008, Avg: 0.0009
Epoch 5/5, Step 60/100, Loss: 0.0008, Avg: 0.0008
Epoch 5/5, Step 80/100, Loss: 0.0007, Avg: 0.0008
============================================================
Epoch 5 完成 - 平均Loss: 0.0008 (↓0.0003)
============================================================
============================================================
✅ 训练完成!
最佳Loss: 0.0008
最终Loss: 0.0008
Loss下降: 10.0000 → 0.0008
峰值显存: 244.33 MB (0.24 GB)
============================================================
训练过程中,仅rank=0每 100 步打印损失值,模型从随机初始化的高损失逐渐下降。
另外,单GPU情况下的训练输出为:
============================================================
单GPU基准测试(无张量并行)
============================================================
使用设备: cuda:0
模型配置:
- Vocab: 1024, Hidden: 512
- Layers: 8, Heads: 8
- 总参数量: 26,793,984
训练任务: 序列记忆
- 训练序列数: 100
- 序列长度: 32
- 词汇表大小: 1024
开始训练...
...
============================================================
✅ 训练完成!
最佳Loss: 0.0023
最终Loss: 0.0023
Loss下降: 10.0000 → 0.0023
峰值显存: 564.16 MB (0.55 GB)
============================================================
TP 的核心优势是降低单卡内存占用。以world_size=4为例,对比单卡训练与 4 卡 TP 的内存峰值:
训练模式 |
单卡内存占用(峰值) |
2 卡 TP 单卡内存占用(峰值) |
内存节省比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
无并行(单卡) |
~564MB |
- |
- |
4 卡 TP |
- |
~244MB |
~56.7% |
总结与思考#
本实验通过可执行的代码深入探讨了 Megatron 风格的 TP 原理与实现,并验证了 TP 在内存节省上的有效性。
核心技术点:
列并行线性层:将权重矩阵按列分割,前向传播需要 All-Gather 操作
行并行线性层:将权重矩阵按行分割,前向传播使用 AllReduce 聚合(已优化autograd)
并行 Attention:将注意力头分布到多个设备,每个设备处理部分头
并行 Embedding:将大型词汇表分割到多个设备,减少单个设备的内存压力